Resistors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistor
![]()

Resistors are measured in Ohms Ω. They are used to limit the current that flows through the circuit. Resistors mostly come in a fixed numeric.
1, 1.5, 2, 2.2, 3.3, 4.7 and then multiples of that. e.g. 1.5kΩ, 2.2MΩ.
The most basic algorithm used with resistors is Ohms law.
v = i * r
Voltage = Current * Resistance.
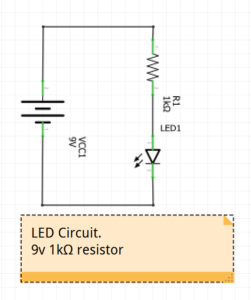
For example if you have a 9v battery and a 1kΩ (1000 ohms) resistor. The current drawn will be:
i = v / r = 9 / 1000 = 9mA (9 milliamps).
If this was in a simple circuit for lighting an LED it would limit the current and hence the brightness of the LED.
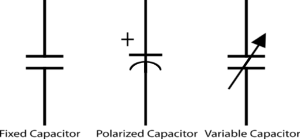
Capacitors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capacitor
Capacitors are measured in Farads (
Transistors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transistor
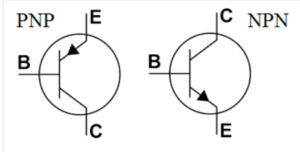
The two basic types of transistors we are covering are NPN and PNP.
Transistor act like switches. If there is a current applied to the base it turns the switch on or off depending on the type.
Diodes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diode

Diodes allow current to pass in only one direction. This means that if they are connected the wrong way around, the the circuit will not work as you expect.
LEDs

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode
Light Emitting Diodes. The symbol for an LED is the symbol for a diode with an added arrow.
Like a diode, current can only pass in one direction through an LED. Unlike a diode, the LED emits light when current passes through it.